Faringoamigdalitis por Streptococo grupo A.docx
Transcript of Faringoamigdalitis por Streptococo grupo A.docx
-
8/10/2019 Faringoamigdalitis por Streptococo grupo A.docx
1/23
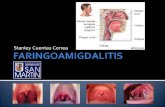
Faringoamigdalitis por Streptococo grupo A
- Inicio abrupto- Odinofagia- Exudado amigdaliano
- Adenopata cervical sensible- Fiebre- Resolucin espontnea en 2-5 das.- Si odinofagia dura ms de 1 semana, en general no es.
- 15-30% de faringitis en nios de 5-15 aos.
- En general en invierno e inicios de primavera.
- Tambin puede acompaarse de cefalea, nuseas y vmitos, dolor
abdominal, disminucin de ingesta oral, petequias palatinas, vula
inflamada, rash escarlatiniforme.
Metas teraputicas para erradicacin del estrepto grupo a de la faringe :
- Reducir la duracin y severidad del cuadro, incluyendo complicacionessupurativas
- Reducir incidencia de complicaciones no-supurativas: ej: fiebrereumtica aguda.
- Reducir transmisin a contactos cercanos al reducir infectividad.
Consideraciones de tratamiento: facilitar administracin Ab y gasto limitado con los
menos efectos adversos posibles.
- Ab es lo ms beneficioso para apurar la resolucin de los sntomas si se daen los 1 2 das de enfermedad.
- Tambin es beneficiosa para reducir las complicaciones supurativas comoabsceso periamigdaliano, linfadenitis cervical y mastoiditis.
- Reduccin complic no-supurativas: principalmente reduce incidencia defiebre reumtica aguda. Rol de Ab en disminuir glomerulonefritis y trastornoneuropsiquitrico peditrico asociado con SGA (PANDAS) no est claro.
- Fiebre reumtica aguda(FRA): aunque los sntomas de faringitis por SGA
se resuelven con Ab, persisten los organismos en el tracto respiratoriosuperior produciendo respuesta inmune que puede conllevar el riesgo defiebre reumtica aguda si la cepa es reumatognica y el husped estgenticamente predispuesto. En alguna poblacin, el S. grupo B y Ctambin podran jugar un rol en patognesis de FRA.
- Prevencin primaria de FRA con penicilina (G). es til si se inicia hasta 9das luego de iniciados los sntomas.
-
8/10/2019 Faringoamigdalitis por Streptococo grupo A.docx
2/23
- Glomerulonefritis: Nios menores de 7 aos parecen tener el mayor riesgode GNPS. El rol del Ab para prevenirla no es claro.
- Transmisin a contactos cercanos es aprox 35%. Ab tiene rol en prevenirlo.luego de 24hrs de tto con penicilina aprox 80% cultivos (-)
Tto:
- Confirmar SGA en faringe por cultivo o test rpido de deteccin antignica(RADT)
- Iniciarlo empricamente, y si los resultados son negativos, suspender.- Tb debe darse en SG-C y G, pero no por 10 das, sino por 5, ya que no se
complican con FRA.
- No hay beneficio para otras bacterias, excepto las raras por:corynebacterium diphteriae y n. gonorrhoeae.
- Historia natural: perodo incubacin 2-4 das, fiebre y sntomasconstitucionales mejoran en 3-4 das. Se observa mejora clnica 48hrsantes en pacientes con PNC vs. placebo en los 1s 2 das de enfermedad.
- Hay preocupacin sobre si la terapia temprana puede reducir la respuestainmune del husped, incrementando el riesgo de faringitis recurrente. Noest indicado retrasar el tratamiento, pero podra ser til en casos deinfeccin recurrente, moderada. Retrasar el tratamiento hasta 9 dastodava el til para prevenir la aparicin de FRA, aunque tal vez menos paralas complicaciones supurativas.
However, this approach should not be considered if
the patient is severely ill or if highly virulent or
rheumatogenic strains are actively circulating within acommunity. Patients are considered no longer
contagious after 24 hours of antibiotic therapy [15].
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/15http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/15http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/15 -
8/10/2019 Faringoamigdalitis por Streptococo grupo A.docx
3/23
-
8/10/2019 Faringoamigdalitis por Streptococo grupo A.docx
4/23
ResistanceAntimicrobial resistance has not been
a significant issue in the treatment of GAS. No clinical
isolate of GAS has demonstrated penicillin
resistance, likely due to the organism's lack of altered
penicillin-binding proteins and/or inefficient gene
transfer mechanisms for resistance [22,23]. However,
streptococcal strains tolerant to penicillin (eg, strains
inhibited but not killed by penicillin in vitro, with ratio
of minimum bactericidal concentration to minimuminhibitory concentration [MIC] of 32) have been
described [24-27]. The clinical significance of such
strains is not clear; they have been isolated in the
setting of outbreaks in which penicillin treatment
failure was observed, but there was no difference in
failure rates among tolerant and susceptible strains.
(See "Antibiotic failure in the treatment of
streptococcal tonsillopharyngitis".)
There have been reports of relatively high levels of
resistance to macrolide antibiotics in some regions;
given the increasing use of macrolides for treatment
of upper and lower respiratory tract infections,
clinicians should be cognizant of local patterns of
antimicrobial resistance [28-37].
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/22,23http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/22,23http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/24-27http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/24-27http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/24-27http://www.uptodate.com/contents/antibiotic-failure-in-the-treatment-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/antibiotic-failure-in-the-treatment-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/antibiotic-failure-in-the-treatment-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/28-37http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/28-37http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/28-37http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/28-37http://www.uptodate.com/contents/antibiotic-failure-in-the-treatment-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/antibiotic-failure-in-the-treatment-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/24-27http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/22,23 -
8/10/2019 Faringoamigdalitis por Streptococo grupo A.docx
5/23
SelectionOralpenicillin Vis the agent of choice
for treatment of GAS pharyngitis given its proven
efficacy, safety, narrow spectrum, and low cost [2,38-
42]. The appropriate duration is 10 days of therapy;
dosing is outlined in the Table (table 1). This
approach is extrapolated from studies performed in
the 1950s demonstrating that treatment of
streptococcal pharyngitis with intramuscular penicillin
prevents acute rheumatic fever [14,20].(See "Treatment and prevention of acute rheumatic
fever".)
Amoxicillinis often used in place of oral penicillin in
children, since the taste of the amoxicillin suspension
is more palatable than that of penicillin. Some datasuggest that oral amoxicillin may be marginally
superior to penicillin, most likely due to better
gastrointestinal (GI) absorption [43,44]. In addition,
amoxicillin has activity against the common
pathogens that cause otitis media (which presents
concurrently with GAS tonsillopharyngitis in up to 15
percent of children, particularly those under four
years of age). Dosing is outlined in the Table (table
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/penicillin-v-potassium-oral-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/penicillin-v-potassium-oral-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/2,38-42http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/2,38-42http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/2,38-42http://www.uptodate.com/content-not-availablehttp://www.uptodate.com/content-not-availablehttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/14,20http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-acute-rheumatic-fever?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-acute-rheumatic-fever?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-acute-rheumatic-fever?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/amoxicillin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/amoxicillin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/43,44http://www.uptodate.com/content-not-availablehttp://www.uptodate.com/content-not-availablehttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/43,44http://www.uptodate.com/contents/amoxicillin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-acute-rheumatic-fever?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-acute-rheumatic-fever?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/14,20http://www.uptodate.com/content-not-availablehttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/2,38-42http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/2,38-42http://www.uptodate.com/contents/penicillin-v-potassium-oral-drug-information?source=see_link -
8/10/2019 Faringoamigdalitis por Streptococo grupo A.docx
6/23
1). (See"Acute otitis media in children: Treatment",
section on 'Initial antimicrobial therapy'.)
Intramuscular penicillin G benzathine(single dose)
may be administered to patients who cannot
complete a 10-day course of oral therapy or to
patients at enhanced risk for rheumatic fever (eg,
those with history of previous rheumatic heart
disease and/or living in crowded conditions).
Injections of benzathine penicillin provide bactericidal
levels against GAS for 21 to 28 days. The addition of
procaine penicillin alleviates some of the discomfort
associated with benzathine injections and may
favorably influence the initial clinical response. The
preferred product in children is the combination of900,000 units of benzathine penicillin G plus 300,000
units of procaine penicillin (Bicillin C-
R 900/300). (SeePenicillin G benzathine-penicillin G
procaine:Drug information). Dosing is outlined in the
Table (table 1).
Cephalosporins are acceptable alternatives in
patients with recurrent GAS infection but are not
recommended as first-line therapy [45-52].
http://www.uptodate.com/content-not-availablehttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/acute-otitis-media-in-children-treatment?source=see_link&anchor=H10#H10http://www.uptodate.com/contents/acute-otitis-media-in-children-treatment?source=see_link&anchor=H10#H10http://www.uptodate.com/contents/acute-otitis-media-in-children-treatment?source=see_link&anchor=H10#H10http://www.uptodate.com/contents/penicillin-g-benzathine-intramuscular-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/penicillin-g-benzathine-and-penicillin-g-procaine-intramuscular-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/penicillin-g-benzathine-and-penicillin-g-procaine-intramuscular-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/penicillin-g-benzathine-and-penicillin-g-procaine-intramuscular-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/penicillin-g-benzathine-and-penicillin-g-procaine-intramuscular-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/content-not-availablehttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/45-52http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/45-52http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/45-52http://www.uptodate.com/content-not-availablehttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/penicillin-g-benzathine-and-penicillin-g-procaine-intramuscular-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/penicillin-g-benzathine-and-penicillin-g-procaine-intramuscular-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/penicillin-g-benzathine-intramuscular-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/acute-otitis-media-in-children-treatment?source=see_link&anchor=H10#H10http://www.uptodate.com/contents/acute-otitis-media-in-children-treatment?source=see_link&anchor=H10#H10http://www.uptodate.com/content-not-available -
8/10/2019 Faringoamigdalitis por Streptococo grupo A.docx
7/23
Cephalosporins have demonstrated better
microbiologic and clinical cure rates than penicillin;
these differences appear to be greater among
children than adults, and some favor use of first-
generation cephalosporins as first-line therapy in this
group [53-55]. However, second- and third-generation
cephalosporins are more expensive than penicillin
and may facilitate development of antibiotic
resistance [46,47]. (See'Recurrent infection'below.)
Antibiotic therapy directed against beta-lactamase
producing upper respiratory tract flora (such
asamoxicillin-clavulanate) remains controversial and
is not indicated in patients with acute pharyngitis
[2,56,57].
For patients with beta-lactam hypersensitivity,
cephalosporins (cefuroxime,cefpodoxime,cefdinir,
andceftriaxone) may be used [38,44-50], in the
absence of history of life-threatening allergic reaction;
cross reactivity with penicillin is less likely for later-generation cephalosporins than first-generation
cephalosporins [45,58-60]. Macrolides
(clarithromycin,azithromycin, or erythromycin) are an
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/53-55http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/53-55http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/53-55http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/46,47http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/46,47http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/46,47http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H16http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H16http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H16http://www.uptodate.com/contents/amoxicillin-and-clavulanate-potassium-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/amoxicillin-and-clavulanate-potassium-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/2,56,57http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/2,56,57http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/2,56,57http://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefuroxime-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefuroxime-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefpodoxime-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefpodoxime-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefdinir-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefdinir-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/ceftriaxone-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/ceftriaxone-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/38,44-50http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/38,44-50http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/38,44-50http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/45,58-60http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/45,58-60http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/45,58-60http://www.uptodate.com/contents/clarithromycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/clarithromycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/clarithromycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/azithromycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/erythromycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/erythromycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/azithromycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/clarithromycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/45,58-60http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/38,44-50http://www.uptodate.com/contents/ceftriaxone-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefdinir-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefpodoxime-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefuroxime-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/2,56,57http://www.uptodate.com/contents/amoxicillin-and-clavulanate-potassium-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H16http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/46,47http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/53-55 -
8/10/2019 Faringoamigdalitis por Streptococo grupo A.docx
8/23
acceptable alternative for penicillin allergic patients,
depending on local resistance patterns [28,31-36].
For the rare patient with an erythromycin-resistant
strain of GAS who is unable to tolerate beta-lactam
agents,clindamycinis an appropriate choice [61].
DurationIn general, the conventional duration of
oral antibiotic therapy to achieve maximal pharyngeal
GAS eradication rates is 10 days, even though
patients usually improve clinically within the first few
days of treatment [62,63]. If penicillin is discontinued
after three days of therapy, the probability of relapse
is higher than if penicillin is discontinued after seven
days of treatment (50 versus 34 percent, respectively)
[14,16,20].
Five days of therapy withcefpodoxime,cefdinir,
orazithromycinis an acceptable alternative
approach, with rates of bacteriologic and clinical cure
of streptococcal pharyngitis comparable with that of
the conventional 10-day course of penicillin [33-36,41,64-76].
Attempts to treat GAS pharyngitis with a single daily
dose of penicillin have been unsuccessful. Although
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/28,31-36http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/28,31-36http://www.uptodate.com/contents/clindamycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/clindamycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/61http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/61http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/62,63http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/14,16,20http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/14,16,20http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/14,16,20http://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefpodoxime-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefpodoxime-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefdinir-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefdinir-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/azithromycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/azithromycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/33-36,41,64-76http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/33-36,41,64-76http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/33-36,41,64-76http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/33-36,41,64-76http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/33-36,41,64-76http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/33-36,41,64-76http://www.uptodate.com/contents/azithromycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefdinir-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefpodoxime-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/14,16,20http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/62,63http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/61http://www.uptodate.com/contents/clindamycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/28,31-36 -
8/10/2019 Faringoamigdalitis por Streptococo grupo A.docx
9/23
some data suggest that once-dailyamoxicillinmay be
sufficient for treatment of GAS pharyngitis, others
have shown that this approach is not adequate for
effective eradication; further investigation is needed
[77-80]. Among the alternative
agents,azithromycinand some cephalosporins
(including cefixime,cefpodoxime,cefadroxil,
andcefdinir) are effective for eradication of
pharyngeal streptococci with once-daily dosing[69,81-84].
Antibiotics for other organismsThe differential
diagnosis of acute pharyngitis is outlined separately
(table 2). (See"Evaluation of acute pharyngitis in
adults".)
The approach to treatment of infection due to
Streptococcus other than group A, influenza,
infectious mononucleosis, primary HIV infection,
Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae,
Chlamydophila pneumoniae, and Corynebacteriumdiphtheriae is discussed separately. (See related
topics.)
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/amoxicillin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/amoxicillin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/amoxicillin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/77-80http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/77-80http://www.uptodate.com/contents/azithromycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/azithromycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefixime-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefixime-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefpodoxime-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefpodoxime-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefadroxil-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefadroxil-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefadroxil-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefdinir-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefdinir-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/69,81-84http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/69,81-84http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/69,81-84http://www.uptodate.com/content-not-availablehttp://www.uptodate.com/content-not-availablehttp://www.uptodate.com/content-not-availablehttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/evaluation-of-acute-pharyngitis-in-adults?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/evaluation-of-acute-pharyngitis-in-adults?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/evaluation-of-acute-pharyngitis-in-adults?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/evaluation-of-acute-pharyngitis-in-adults?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/evaluation-of-acute-pharyngitis-in-adults?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/evaluation-of-acute-pharyngitis-in-adults?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/content-not-availablehttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/69,81-84http://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefdinir-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefadroxil-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefpodoxime-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefixime-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/azithromycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/77-80http://www.uptodate.com/contents/amoxicillin-drug-information?source=see_link -
8/10/2019 Faringoamigdalitis por Streptococo grupo A.docx
10/23
The approach to treatment of infection due to F.
necrophorum is uncertain; further study is needed to
better define the role of F. necrophorum in the
epidemiology of pharyngitis and the associated risk
between F. necrophorum pharyngitis and Lemierres
syndrome. Some favor empiric treatment with
penicillins or cephalosporins in the setting of negative
diagnostic test results but at least three Centor
criteria (fever, tonsillar exudate, swollen tendercervical adenopathy, or lack of cough) among
patients 15 to 30 years of age, although it is uncertain
whether this approach is effective for prevention of
Lemierres syndrome [85,86]. Therefore, we favor
antibiotic therapy for pharyngitis only in the setting of
positive diagnostic data [41]. (See"Suppurative
(septic) thrombophlebitis", section on 'Jugular
vein'and"Evaluation of acute pharyngitis in adults",
section on 'Evaluation'.)
The antibiotics of choice for treatment of infection due
to Arcanobacterium haemolyticum
areerythromycinorazithromycin; data are limited to
case reports and in vitro studies [87,88]. In vitro
studies show most strains to be susceptible to beta-
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/85,86http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/85,86http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/41http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/41http://www.uptodate.com/contents/suppurative-septic-thrombophlebitis?source=see_link&anchor=H11#H11http://www.uptodate.com/contents/suppurative-septic-thrombophlebitis?source=see_link&anchor=H11#H11http://www.uptodate.com/contents/suppurative-septic-thrombophlebitis?source=see_link&anchor=H11#H11http://www.uptodate.com/contents/suppurative-septic-thrombophlebitis?source=see_link&anchor=H11#H11http://www.uptodate.com/contents/evaluation-of-acute-pharyngitis-in-adults?source=see_link&anchor=H316692798#H316692798http://www.uptodate.com/contents/evaluation-of-acute-pharyngitis-in-adults?source=see_link&anchor=H316692798#H316692798http://www.uptodate.com/contents/evaluation-of-acute-pharyngitis-in-adults?source=see_link&anchor=H316692798#H316692798http://www.uptodate.com/contents/evaluation-of-acute-pharyngitis-in-adults?source=see_link&anchor=H316692798#H316692798http://www.uptodate.com/contents/erythromycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/erythromycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/erythromycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/azithromycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/azithromycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/87,88http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/87,88http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/87,88http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/87,88http://www.uptodate.com/contents/azithromycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/erythromycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/evaluation-of-acute-pharyngitis-in-adults?source=see_link&anchor=H316692798#H316692798http://www.uptodate.com/contents/evaluation-of-acute-pharyngitis-in-adults?source=see_link&anchor=H316692798#H316692798http://www.uptodate.com/contents/suppurative-septic-thrombophlebitis?source=see_link&anchor=H11#H11http://www.uptodate.com/contents/suppurative-septic-thrombophlebitis?source=see_link&anchor=H11#H11http://www.uptodate.com/contents/suppurative-septic-thrombophlebitis?source=see_link&anchor=H11#H11http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/41http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/85,86 -
8/10/2019 Faringoamigdalitis por Streptococo grupo A.docx
11/23
lactam agents, although treatment failure may occur
because of poor penetration into the intracellular
space [88].Clindamycin,doxycycline,ciprofloxacin,
andvancomycinare also effective agents.
Follow-upPatients with GAS pharyngitis should
have improvement in clinical symptoms within three
to four days of initiating antibiotic therapy. Failure to
observe a clinical response to antibiotics should
prompt diagnostic reconsideration or the possibility of
a suppurative complication. If acute streptococcal
pharyngitis was diagnosed by rapid testing, the result
may represent a false-positive finding; if the diagnosis
was made by culture, the patient may be a
pharyngeal carrier whose symptoms are likelyattributable to an alternate process.
(See 'Carriers'below.)
In general, test of cure is not necessary for
asymptomatic patients or their close contacts
following completion of a course of antimicrobialtherapy. The majority of patients with GAS remaining
in their upper respiratory tracts after completing a
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/88http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/88http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/88http://www.uptodate.com/contents/clindamycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/clindamycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/doxycycline-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/doxycycline-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/doxycycline-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/ciprofloxacin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/ciprofloxacin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/vancomycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/vancomycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H18http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H18http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H18http://www.uptodate.com/contents/vancomycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/ciprofloxacin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/doxycycline-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/clindamycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/88 -
8/10/2019 Faringoamigdalitis por Streptococo grupo A.docx
12/23
course of antimicrobial therapy are Streptococcus
carriers [89,90].
However, follow-up test of cure is appropriate testing
for asymptomatic index patients and their
asymptomatic household contacts in the following
circumstances:
Individuals with history of rheumatic fever
Individuals who develop acute pharyngitis
during an outbreak of acute rheumatic fever or
acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis [90]
Spread of GAS among several family
members
Asymptomatic patients and asymptomatic household
contacts in the above circumstances with positive
laboratory results should receive a standard course of
antimicrobial therapy with one of the agents outlined
above [91]. Repeat treatment should be administered
with an agent with greater beta-lactamase stability
than the previous agent [56]. If a penicillin was used
for initial therapy, repeat treatment withamoxicillin-
clavulanateor a first-generation cephalosporin may
be used; if initial treatment was with a first generation
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/89,90http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/89,90http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/89,90http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/90http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/90http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/91http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/91http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/56http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/56http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/56http://www.uptodate.com/contents/amoxicillin-and-clavulanate-potassium-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/amoxicillin-and-clavulanate-potassium-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/amoxicillin-and-clavulanate-potassium-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/amoxicillin-and-clavulanate-potassium-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/amoxicillin-and-clavulanate-potassium-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/56http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/91http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/90http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/89,90 -
8/10/2019 Faringoamigdalitis por Streptococo grupo A.docx
13/23
cephalosporin, a second or third generation
cephalosporin may be used. (See"Evaluation of
acute pharyngitis in adults"and'Antibiotics for group A
Streptococcus'above.)
Recurrent infectionIn the setting of recurrent
acute pharyngitis with positive repeat diagnostic
testing, there are several possible explanations
[89,91,92]:
Persistence of Streptococcus carriage in the
setting of viral infection
Nonadherence with the prescribed
antimicrobial regimen
New infection with GAS acquired from
household or community contacts
Treatment failure (eg, repeat episode of
pharyngitis caused by the original infecting
strain); treatment failure is rare.
In the setting of a second episode of acute
pharyngitis with positive repeat diagnostic testing, a
repeat course of treatment is appropriate (table 1).
Repeat treatment should be administered with an
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/evaluation-of-acute-pharyngitis-in-adults?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/evaluation-of-acute-pharyngitis-in-adults?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/evaluation-of-acute-pharyngitis-in-adults?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H11http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H11http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H11http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/89,91,92http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/89,91,92http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/89,91,92http://www.uptodate.com/content-not-availablehttp://www.uptodate.com/content-not-availablehttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/89,91,92http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H11http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H11http://www.uptodate.com/contents/evaluation-of-acute-pharyngitis-in-adults?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/evaluation-of-acute-pharyngitis-in-adults?source=see_link -
8/10/2019 Faringoamigdalitis por Streptococo grupo A.docx
14/23
agent with greater beta-lactamase stability than the
previous agent [56].
If adherence is uncertain, intramuscularpenicillin G
benzathinemay be chosen as the second course of
therapy. If a full course of penicillin was completed as
initial therapy, a first-generation cephalosporin (such
ascephalexin,cefadroxil) may be used; if a first-
generation cephalosporin was used for initial therapy,
a second- or third-generation cephalosporin (such
ascefpodoxime,cefdinir) may be used. Alternative
agents include amoxicillin-clavulanateor clindamycin.
It is not necessary to perform follow-up testing after
the second course of therapy unless the patient
remains or becomes symptomatic or unless special
circumstances as outlined above are present.
(See 'Antibiotics for group A Streptococcus'above
and'Follow-up'above.)
In the setting of multiple recurrent episodes, it may be
difficult to distinguish true GAS pharyngitis from viral
pharyngitis in the setting of streptococcal carriage. It
is likely that most of these patients are carriers
experiencing nonstreptococcal infections. This may
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/56http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/56http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/56http://www.uptodate.com/contents/penicillin-g-benzathine-intramuscular-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/penicillin-g-benzathine-intramuscular-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/penicillin-g-benzathine-intramuscular-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cephalexin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cephalexin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cephalexin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefadroxil-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefadroxil-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefpodoxime-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefpodoxime-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefdinir-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefdinir-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/amoxicillin-and-clavulanate-potassium-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/clindamycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/clindamycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H11http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H15http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H15http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H15http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H15http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H11http://www.uptodate.com/contents/clindamycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/amoxicillin-and-clavulanate-potassium-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefdinir-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefpodoxime-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cefadroxil-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/cephalexin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/penicillin-g-benzathine-intramuscular-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/penicillin-g-benzathine-intramuscular-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/56 -
8/10/2019 Faringoamigdalitis por Streptococo grupo A.docx
15/23
be discernible by evaluating for the presence of GAS
during asymptomatic intervals and/or by typing
streptococcal isolates obtained during distinct
episodes (with the expertise of a specialized
laboratory). In these circumstances, treatment
withclindamycinor amoxicillin-clavulanatemay be
beneficial since these agents have demonstrated high
eradication rates for pharyngeal streptococci (table 1)
[56,61,93]. (See'Carriers'below.)
For patients with as many as six GAS infections in a
single year or three to four episodes in two
consecutive years, tonsillectomy may be an
appropriate therapeutic consideration [94,95]. This
was illustrated in a randomized trial including 187children with recurrent pharyngitis, of whom 95 were
managed with tonsillectomy [94]. The incidence of
pharyngitis during the first two years of follow-up was
significantly lower among the tonsillectomy group.
(See "Tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy in children:
Indications and contraindications", section on
'Recurrent infection'.)
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/clindamycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/clindamycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/amoxicillin-and-clavulanate-potassium-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/content-not-availablehttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/56,61,93http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/56,61,93http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/56,61,93http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H18http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H18http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/94,95http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/94,95http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/94,95http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/94http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/94http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/94http://www.uptodate.com/contents/tonsillectomy-and-adenoidectomy-in-children-indications-and-contraindications?source=see_link&anchor=H7#H7http://www.uptodate.com/contents/tonsillectomy-and-adenoidectomy-in-children-indications-and-contraindications?source=see_link&anchor=H7#H7http://www.uptodate.com/contents/tonsillectomy-and-adenoidectomy-in-children-indications-and-contraindications?source=see_link&anchor=H7#H7http://www.uptodate.com/contents/tonsillectomy-and-adenoidectomy-in-children-indications-and-contraindications?source=see_link&anchor=H7#H7http://www.uptodate.com/contents/tonsillectomy-and-adenoidectomy-in-children-indications-and-contraindications?source=see_link&anchor=H7#H7http://www.uptodate.com/contents/tonsillectomy-and-adenoidectomy-in-children-indications-and-contraindications?source=see_link&anchor=H7#H7http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/94http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/94,95http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H18http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/56,61,93http://www.uptodate.com/content-not-availablehttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/amoxicillin-and-clavulanate-potassium-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/clindamycin-drug-information?source=see_link -
8/10/2019 Faringoamigdalitis por Streptococo grupo A.docx
16/23
Antibiotic failure in the treatment of streptococcal
tonsillopharyngitis is discussed separately.
(See "Antibiotic failure in the treatment of
streptococcal tonsillopharyngitis".)
PREVENTION
CarriersIn general, group A Streptococcus (GAS)
resides in the oropharynx of Streptococcus carriers in
the absence of host immunologic response to theorganism [96]. In temperate climates during the winter
and spring, up to 20 percent of asymptomatic school-
aged children may be carriers. About 25 percent of
asymptomatic individuals in the households of index
patients harbor GAS in their upper respiratory tracts
[91]. Streptococcal carriage may persist for many
months. (See"Antibiotic failure in the treatment of
streptococcal tonsillopharyngitis", section on
'Streptococcal carriage'.)
Carriers may demonstrate evidence of GAS in the
upper respiratory tract during an episode of viral
pharyngitis, suggesting acute streptococcal
pharyngitis. In these circumstances, clinically
distinguishing viral from streptococcal pharyngitis can
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/antibiotic-failure-in-the-treatment-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/antibiotic-failure-in-the-treatment-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/antibiotic-failure-in-the-treatment-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/96http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/96http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/91http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/91http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/91http://www.uptodate.com/contents/antibiotic-failure-in-the-treatment-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=see_link&anchor=H12#H12http://www.uptodate.com/contents/antibiotic-failure-in-the-treatment-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=see_link&anchor=H12#H12http://www.uptodate.com/contents/antibiotic-failure-in-the-treatment-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=see_link&anchor=H12#H12http://www.uptodate.com/contents/antibiotic-failure-in-the-treatment-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=see_link&anchor=H12#H12http://www.uptodate.com/contents/antibiotic-failure-in-the-treatment-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=see_link&anchor=H12#H12http://www.uptodate.com/contents/antibiotic-failure-in-the-treatment-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=see_link&anchor=H12#H12http://www.uptodate.com/contents/antibiotic-failure-in-the-treatment-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=see_link&anchor=H12#H12http://www.uptodate.com/contents/antibiotic-failure-in-the-treatment-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=see_link&anchor=H12#H12http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/91http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/96http://www.uptodate.com/contents/antibiotic-failure-in-the-treatment-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/antibiotic-failure-in-the-treatment-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=see_link -
8/10/2019 Faringoamigdalitis por Streptococo grupo A.docx
17/23
be difficult. Useful clues may include patient age,
season, local epidemiology, and the nature of
presenting signs and symptoms. In addition,
pharyngeal strep carriers tend to have very low
antistreptolysin O (ASO) titers; they may be just
above detectable. (See"Evaluation of acute
pharyngitis in adults".)
Streptococcus carriers are unlikely to spread the
organism to close contacts and are at very low risk for
developing suppurative complications or acute
rheumatic fever [96]. Moreover, eradication of GAS
from the upper respiratory tract of carriers is much
more difficult than eradication of GAS from patients
with acute infection [50,89,97]. In general, except forthe circumstances described above, streptococcus
carriers do not require antimicrobial therapy.
(See 'Follow-up'above.)
Foodborne illnessStreptococcal contamination of
food has been implicated in foodborne outbreaks ofpharyngitis [98-102], and foodborne transmission of
GAS pharyngitis by asymptomatic food service
workers with nasopharyngeal carriage has been
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/evaluation-of-acute-pharyngitis-in-adults?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/evaluation-of-acute-pharyngitis-in-adults?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/evaluation-of-acute-pharyngitis-in-adults?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/evaluation-of-acute-pharyngitis-in-adults?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/96http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/96http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/50,89,97http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/50,89,97http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H15http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/98-102http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/98-102http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/98-102http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H15http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/50,89,97http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/96http://www.uptodate.com/contents/evaluation-of-acute-pharyngitis-in-adults?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/evaluation-of-acute-pharyngitis-in-adults?source=see_link -
8/10/2019 Faringoamigdalitis por Streptococo grupo A.docx
18/23
reported [101,103,104]. Factors that can reduce
foodborne transmission of GAS pharyngitis include
thorough cooking, complete reheating, and use of
gloves while handling food [98,105].
ProphylaxisContinuous antimicrobial prophylaxis
is only appropriate for prevention of recurrent
rheumatic fever in patients who have experienced a
previous episode of rheumatic fever. (See"Treatment
and prevention of acute rheumatic fever", section on
'Secondary prevention'.)
VaccinationThere is no vaccine against GAS
available for clinical use, although development of
this preventive measure is under investigation
[106,107]. An important area of uncertainty is whether
vaccine-induced antibodies may cross-react with host
tissue to produce nonsuppurative sequelae in the
absence of clinical infection.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTSUpToDate offers
two types of patient education materials, The Basics
and Beyond the Basics. The Basics patient
education pieces are written in plain language, at the
5thto 6
thgrade reading level, and they answer the
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/101,103,104http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/101,103,104http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/101,103,104http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/98,105http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/98,105http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-acute-rheumatic-fever?source=see_link&anchor=H8#H8http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-acute-rheumatic-fever?source=see_link&anchor=H8#H8http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-acute-rheumatic-fever?source=see_link&anchor=H8#H8http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-acute-rheumatic-fever?source=see_link&anchor=H8#H8http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-acute-rheumatic-fever?source=see_link&anchor=H8#H8http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/106,107http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/106,107http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/106,107http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/106,107http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-acute-rheumatic-fever?source=see_link&anchor=H8#H8http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-acute-rheumatic-fever?source=see_link&anchor=H8#H8http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-acute-rheumatic-fever?source=see_link&anchor=H8#H8http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/98,105http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis/abstract/101,103,104 -
8/10/2019 Faringoamigdalitis por Streptococo grupo A.docx
19/23
four or five key questions a patient might have about
a given condition. These articles are best for patients
who want a general overview and who prefer short,
easy-to-read materials. Beyond the Basics patient
education pieces are longer, more sophisticated, and
more detailed. These articles are written at the 10thto
12thgrade reading level and are best for patients who
want in-depth information and are comfortable with
some medical jargon.
Here are the patient education articles that are
relevant to this topic. We encourage you to print or e-
mail these topics to your patients. (You can also
locate patient education articles on a variety of
subjects by searching on patient info and thekeyword(s) of interest.)
Basics topics (see"Patient information: Sore
throat in adults (The Basics)"and"Patient
information: Strep throat in children (The
Basics)"and"Patient information: Scarlet fever(The Basics)")
Beyond the Basics topics (see "Patient
information: Sore throat in children (Beyond the
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/sore-throat-in-adults-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/sore-throat-in-adults-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/sore-throat-in-adults-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/sore-throat-in-adults-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/strep-throat-in-children-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/strep-throat-in-children-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/strep-throat-in-children-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/strep-throat-in-children-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/strep-throat-in-children-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/scarlet-fever-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/scarlet-fever-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/scarlet-fever-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/sore-throat-in-children-beyond-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/sore-throat-in-children-beyond-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/sore-throat-in-children-beyond-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/sore-throat-in-children-beyond-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/scarlet-fever-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/scarlet-fever-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/strep-throat-in-children-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/strep-throat-in-children-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/strep-throat-in-children-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/sore-throat-in-adults-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/sore-throat-in-adults-the-basics?source=see_link -
8/10/2019 Faringoamigdalitis por Streptococo grupo A.docx
20/23
Basics)"and"Patient information: Sore throat in
adults (Beyond the Basics)")
SUMMARY AND RECOMMENDATIONS
Goals of antimicrobial therapy for eradication
of group A Streptococcus (GAS) from the
pharynx in the setting of acute streptococcal
pharyngitis include (see'Goals of
therapy'above):
Reducing duration and severity of clinical
signs and symptoms, including
suppurative complications
Reducing incidence of nonsuppurative
complications (eg, acute rheumatic fever)
Reducing transmission to close contacts
by reducing infectivity
We recommend initiating treatment with
antimicrobial therapy for patients with
symptomatic pharyngitis if the presence of
group A streptococci in the pharynx is confirmedby culture or rapid antigen detection testing
(RADT) (Grade 1A). (See'Treatment'above.)
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/sore-throat-in-children-beyond-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/sore-throat-in-children-beyond-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/sore-throat-in-adults-beyond-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/sore-throat-in-adults-beyond-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/sore-throat-in-adults-beyond-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/sore-throat-in-adults-beyond-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H2http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H2http://www.uptodate.com/contents/grade/1?title=Grade%201A&topicKey=ID/8049http://www.uptodate.com/contents/grade/1?title=Grade%201A&topicKey=ID/8049http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H9http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H9http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H9http://www.uptodate.com/contents/grade/1?title=Grade%201A&topicKey=ID/8049http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H2http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H2http://www.uptodate.com/contents/sore-throat-in-adults-beyond-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/sore-throat-in-adults-beyond-the-basics?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/sore-throat-in-children-beyond-the-basics?source=see_link -
8/10/2019 Faringoamigdalitis por Streptococo grupo A.docx
21/23
We suggest initiating treatment with
antimicrobial therapy for patients whose
clinical and/or epidemiologic factors point to a
high index of suspicion for GAS pharyngitis
while laboratory results are pending (Grade
2B). (See 'Treatment'above.)
Oral penicillin Vis the agent of choice for
treatment of GAS pharyngitis in many clinical
settings given its proven efficacy, safety, narrowspectrum, and low cost.Amoxicillinis often used
in place of oral penicillin in children, since the
taste of the amoxicillin suspension is more
palatable than that of penicillin (table 1). First-
generation cephalosporins are an acceptable
alternative to penicillin and amoxicillin in the
setting of treatment failure or beta-lactam
hypersensitivity. (See'Selection'above.)
Although most patients improve clinically
within the first few days of treatment, the
conventional duration of oral antibiotic therapyis 10 days to achieve maximal pharyngeal GAS
eradication rates. Intramuscular penicillin G
benzathinemay be administered to patients
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/grade/5?title=Grade%202B&topicKey=ID/8049http://www.uptodate.com/contents/grade/5?title=Grade%202B&topicKey=ID/8049http://www.uptodate.com/contents/grade/5?title=Grade%202B&topicKey=ID/8049http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H9http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H9http://www.uptodate.com/contents/penicillin-v-potassium-oral-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/penicillin-v-potassium-oral-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/amoxicillin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/amoxicillin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/content-not-availablehttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H13http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H13http://www.uptodate.com/contents/penicillin-g-benzathine-intramuscular-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/penicillin-g-benzathine-intramuscular-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/penicillin-g-benzathine-intramuscular-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/penicillin-g-benzathine-intramuscular-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H13http://www.uptodate.com/content-not-availablehttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/amoxicillin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/penicillin-v-potassium-oral-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H9http://www.uptodate.com/contents/grade/5?title=Grade%202B&topicKey=ID/8049http://www.uptodate.com/contents/grade/5?title=Grade%202B&topicKey=ID/8049 -
8/10/2019 Faringoamigdalitis por Streptococo grupo A.docx
22/23
who cannot complete a 10-day course of oral
therapy. (See 'Duration'above.)
We suggest NOT treating with antibiotics forpharyngitis in the absence of positive diagnostic
culture data (Grade 2C). We
suggesterythromycinorazithromycinfor
treatment of pharyngitis due to A. haemolyticum
(Grade 2C). (See'Antibiotics for other
organisms'above.)
In general, test of cure is not necessary for
asymptomatic patients or their close contacts
following completion of a course of antimicrobial
therapy, except in unique circumstances.
(See 'Follow-up'above.)
We suggest a repeat course of treatment for
patients with a repeat episode of acute
pharyngitis and positive repeat diagnostic
testing (Grade 2C). Patients warranting a
repeat course of treatment may receive an
agent with greater beta-lactamase stability thanthe previous agent. (See'Recurrent
infection'above.)
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H14http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H14http://www.uptodate.com/contents/grade/6?title=Grade%202C&topicKey=ID/8049http://www.uptodate.com/contents/grade/6?title=Grade%202C&topicKey=ID/8049http://www.uptodate.com/contents/erythromycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/erythromycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/erythromycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/azithromycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/azithromycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/grade/6?title=Grade%202C&topicKey=ID/8049http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H27287700http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H27287700http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H27287700http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H27287700http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H15http://www.uptodate.com/contents/grade/6?title=Grade%202C&topicKey=ID/8049http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H16http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H16http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H16http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H16http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H16http://www.uptodate.com/contents/grade/6?title=Grade%202C&topicKey=ID/8049http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H15http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H27287700http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H27287700http://www.uptodate.com/contents/grade/6?title=Grade%202C&topicKey=ID/8049http://www.uptodate.com/contents/azithromycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/erythromycin-drug-information?source=see_linkhttp://www.uptodate.com/contents/grade/6?title=Grade%202C&topicKey=ID/8049http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H14 -
8/10/2019 Faringoamigdalitis por Streptococo grupo A.docx
23/23
Patients who are long-term streptococcal
carriers may develop multiple episodes of
pharyngitis due to viral infection. In such cases,
repeatedly positive cultures or rapid antigen
tests for GAS may be misleading, and further
treatment for streptococcal pharyngitis may not
be warranted. Carriers are unlikely to spread
the organism to close contacts and are at very
low risk for developing suppurativecomplications or acute rheumatic fever.
Moreover, eradication of GAS from the upper
respiratory tract of carriers can be difficult and is
not necessary. (See'Carriers'above.)
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H18http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H18http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcal-tonsillopharyngitis?source=search_result&search=faringoamigdalitis+bacteriana&selectedTitle=2%7E150#H18