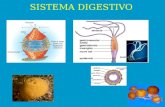
SISTEMA DIGESTÓRIO
-
Upload
marshall-knapp -
Category
Documents
-
view
23 -
download
0
description
Transcript of SISTEMA DIGESTÓRIO

SISTEMA DIGESTÓRIO


O Trato Gastrointestinal (TGI)
http://connection.lww.com/Products/stedmansmedict/primalpictures.asp

Los órganos de la digestión
http://www.icarito.cl/icarito/enciclopedia/canal/canal/0,0,38035857_152308935,00.html

Los órganos de la digestión
http://www.icarito.cl/icarito/enciclopedia/canal/canal/0,0,38035857_152308935,00.html

As grandes funções do Sistema Digestório:Motilidade, digestão, secreção, absorção e excreção.
Silverthorn 2nd EDITION http://cwx.prenhall.com/bookbind/pubbooks/silverthorn2/medialib/Image_Bank/html/custom20.html


Vander, Sherman & Luciano, 1997Vander, Sherman & Luciano, 1997
As grandes funções do Sistema Digestório:Motilidade, digestão, secreção, absorção e excreção.
extraído de: Vander, Sherman & Luciano, 2002 – WEBsite original: http://www.biocourse.com/mhhe/bcc/domains/quad/topic.xsp?id=000270


MOTILIDADEMOTILIDADE
DUAS FUNÇÕES: MOVIMENTAR O ALIMENTO – BOCA – ANUSDUAS FUNÇÕES: MOVIMENTAR O ALIMENTO – BOCA – ANUS
MISTURAR E QUEBRAR MECANICAMENTEMISTURAR E QUEBRAR MECANICAMENTE
CARACTERÍSTICAS DO MUSCULO LISO GICARACTERÍSTICAS DO MUSCULO LISO GI
• JUNÇÕES COMUNICANTES – SEGMENTOS DE CONTRAÇÃOJUNÇÕES COMUNICANTES – SEGMENTOS DE CONTRAÇÃO
• CONTRAÇOES TÔNICAS (HORAS– EX. ESFINCTERES )CONTRAÇOES TÔNICAS (HORAS– EX. ESFINCTERES )
• CONTRAÇÕES FÁSICAS ( POUCOS SEGUNDOS )CONTRAÇÕES FÁSICAS ( POUCOS SEGUNDOS )
• CICLO CONTRAÇÃO E RELAXAMENTO – POTENCIAIS DE ONDAS CICLO CONTRAÇÃO E RELAXAMENTO – POTENCIAIS DE ONDAS LENTAS (ORIGEM – CELS INTERSTICIAIS DE CAJAL)LENTAS (ORIGEM – CELS INTERSTICIAIS DE CAJAL)
FREQUENCIA: 3 ONDAS/MIN NO ESTOMAGOFREQUENCIA: 3 ONDAS/MIN NO ESTOMAGO
12 ONDAS/MIN NO DUODENO12 ONDAS/MIN NO DUODENO

TRÊS FORMAS GERAIS DE MOVIMENTOS
1. COMPLEXO DE MIGRAÇÃO MOTORA –
- DO ESTÔMAGO AO INTESTINO – LEVA 90 MINUTOS - VARRE O ALIMENTO RESTANTE E BACTERIAS DO TGI PARA O INTESTINO GROSSO – FUNÇÃO DE LIMPEZA
2. CONTRÇÕES PERISTÁLTICAS – APOS AS REFEIÇÕES
ANEL DE CONTRAÇÃO EMPURRA O BOLO ALIMENTAR 2 A 25 M/S
HORMONIOS, SUBSTANCIAS PARACRINAS E SNA INFLUENCIAM
3. CONTRAÇÕES SEGMENTARES
- PEQUENOS SEGMENTOS (1 A 5 CM) CONTRAEM E RELAXAM – DIREÇÃO ORAL-ABORAL
4. HAUSTRAÇÕES
- MOVIMENTOS SEGMENTARES ESPECÍFICOS DO INTESTINO GROSSO




MOTILIDADE GASTROINTESTINAL: mistura e deslocamento do alimento ao longo do trato.
Movimentos de MisturaMovimentos de Mistura Movimentos PropulsivosMovimentos Propulsivos***************PADRÕES DE MOTILIDADE NO
TRATO*******************************PADRÕES DE MOTILIDADE NO
TRATO****************

O TUBO DIGESTÓRIO
E SUAS PRINCIPAIS
ESTRUTURAS



Veja mais sobre este assunto através de animações online em:
http://www.interactivephysiology.com/login/digestdemo/systems/buildframes.html?digestive/contdig/01
O SISTEMA NERVOSO ENTÉRICO

O tubo digestório e suas principais estruturas
extraído de: Vander, Sherman & Luciano, 2002 – WEBsite original: http://www.biocourse.com/mhhe/bcc/domains/quad/topic.xsp?id=000270

O tubo digestório e suas principais estruturas
Extraído do artigo: The Enteric Nervous System: A Second Brain, GERSHON, M. D. - Columbia University, 1999; extraído, quando disponível (2002) de: http://www.hosppract.com/issues/1999/07/gershon.htm

O SISTEMA NERVOSO ENTÉRICO
Major neural plexuses of the small intestine. (A, Seen in whole mounts; B, seen in transverse section next) The two ganglionated plexuses are the myenteric and submucosal plexuses. Fibers originating in the myenteric and submucosal plexuses form the nonganglionated plexuses: the tertiary plexus (which innervates the longitudinal layer of muscularis externa), the deep muscular plexus (which supplies the inner dense circular muscle), and the mucosal plexus. Neurons and neuronal processes are shown in color. (Redrawn from Furness JB, Costal M: Neuroscience 5:1, 1980.) Berne et al., 2004
veja também em: Furness, 2005 (disponivel no “Google Pesquisa de Livros”)

O SISTEMA NERVOSO ENTÉRICO
Fig. 31-4B Major neural plexuses of the small intestine. (A, Seen in whole mounts; B, seen in transverse section.) The two ganglionated plexuses are the myenteric and submucosal plexuses. Fibers originating in the myenteric and submucosal plexuses form the nonganglionated plexuses: the tertiary plexus (which innervates the longitudinal layer of muscularis externa), the deep muscular plexus (which supplies the inner dense circular muscle), and the mucosal plexus. Neurons and neuronal processes are shown in color. (Redrawn from Furness JB, Costal M: Neuroscience 5:1, 1980.)
Berne et al., 2004veja também em: Furness, 2005 (disponivel no “Google Pesquisa de Livros”)

http://academic.kellogg.cc.mi.us/herbrandsonc/bio201_McKinley/Nervous%20System.htm
Modulação das
atividades doSistema
Digestório:
PARASSIMPÁTICO

http://academic.kellogg.cc.mi.us/herbrandsonc/bio201_McKinley/Nervous%20System.htm
Modulação das
atividades doSistema
Digestório:
SIMPÁTICO

Modulação das
atividades doSistema
Digestório:
SIMPÁTICO
e
PARASSIMPÁTICO
Purves, 2001. Veja livro na íntegra online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=.0GeCIZUt-B54vyeAe4Hyry4Zb0zEqjWqkCmuVa5k

Modulação das atividades do Sistema Digestório pelosSistema Nervoso Parassimpático e Simpático
Veja mais sobre este assunto através de animações online em: http://www.interactivephysiology.com/login/digestdemo/systems/buildframes.html?digestive/contdig/01

Veja mais sobre este assunto através de animações online em:
http://www.interactivephysiology.com/login/digestdemo/systems/buildframes.html?digestive/contdig/01
Modulação das atividades do Sistema Digestório pelosSistema Nervoso Parassimpático e Simpático

Modulação das
atividades do Sistema Digestório:
PS e SP
Levy et al., 2006 “Berne e Levy: Princípios de Fisiologia”, 4ª Ed. Elsevier
Major features of the autonomic innervation of the gastrointestinal tract. In most cases the autonomic nerves influence the functions of the gastrointestinal tract by modulating the activities of neurons of the enteric nervous system.

ações fisiológicas
VIP (peptídeo intestinal vasoativo) () contração (ou relaxa) músculos lisos do TGI e das arteríolas
Encefalinas (met- e leu-encefalina) (+) tônus (ou contração) dos esfíncteres
neuromoduladores:NO (óxido nítrico)NPY (neuropeptídeo Y)
() contração (ou relaxa) músculos lisos da
camada circular e dos esfíncteres
GRP (peptídeo liberador de Gastrina) (+) liberação de Gastrina
EXEMPLOS DE NEUROTRANSMISSORES OU NEUROMODULADORES DO TGI DO TIPO “NANC” (NÃO-ADRENÉRGICO/NÃO-COLINÉRGICO):

programas motores
inibidores
excitadores
SISTEMA NERVOSO ENTÉRICO Sistemas efetores
neurônios sensoriais
interneurôniosneurônios motores
SISTEMA NERVOSO CENTRAL
epitélio mucoso
músculos lisos
vasos sangüíneos
células secretoras
(endócrinas e exócrinas)
quimioceptores
mecanoceptores
termoceptores
circuitos integradores
MODELO CONCEITUAL DO SISTEMA NERVOSO ENTÉRICO E A REGULAÇÃO DAS FUNÇÕES DO TGI
modificado de: http://library.med.utah.edu/physio/5200GI_lectures/motility.swf

programas motores
inibidores
excitadores
SISTEMA NERVOSO ENTÉRICO Sistemas efetores
neurônios sensoriais
interneurôniosneurônios motores
substância endócrina ou
parácrinasubstâncias presentes na luz da víscera
Estímulos no lúmen eliciam reflexos vago-vagais (alça longa) e locais (alça curta) os quais ativam programas motores específicos do SNE.
epitélio mucoso
músculos lisos
vasos sangüíneos
células secretoras
(endócrinas e exócrinas)
quimioceptores
mecanoceptores
termoceptores
SISTEMA NERVOSO CENTRAL
circuitos integradores
MODELO CONCEITUAL DO SISTEMA NERVOSO ENTÉRICO E A REGULAÇÃO DAS FUNÇÕES DO TGI
modificado de: http://library.med.utah.edu/physio/5200GI_lectures/motility.swf

REFLEXOS DE CONTROLE GASTROINTESTINAL
SISTEMA NERVOSO CENTRALSISTEMA NERVOSO CENTRAL
centros de integraçãocentros de integração
GÂNGLIOS AUTONÔMICOSGÂNGLIOS AUTONÔMICOS
PLEXO MIOENTÉRICOPLEXO MIOENTÉRICO
PLEXO SUBMUCOSOPLEXO SUBMUCOSO
RECEPTORESQuimiorreceptores e mecanorreceptores da parede do tubo digestório
EFETORES músculo liso, vasos sanguíneos,
células endócrinas/exócrinas,da parede do tubo digestivo
REFLEXO LOCAL
REFLEXO CURTO
REFLEXO LONGO

3. LONG-RANGE REFLEXES - altogether different types of rflexes which involve co-ordinated response of one region of the gut wall following activation in other parts of the GIT.1. Gastro-enteric reflex - distension of stomach increase the excitability (motor and secretory) of the small intestine. 2. Gastro-ileal reflex - distension of stomach intesifies the activity of the terminal ileum and opens the ileo-cecal sphincter3. Gastro- and duodeno-colic reflexes (with participation of extrinsic innervation and also hormonal (gastrin)`). Distension of stomach or duodenum initiate 'mass movements' of the colon.4. Ileo-gastric reflex - distension of an ileal segment inhibits gastric motility.5. Intestino-intestinal reflex - cessation of intestinal motility upon excessive distention (adynamic ileus), or rough handling (surgery) or peritonitis (severe irritation)
Reflexos do sistema nervoso entérico
extraído, enquanto disponível, de: http://medweb.bham.ac.uk/research/toescu/Teaching/GIT/OutlineDetailsMeds.htm#anchor225964


ENCHIMENTO
GÁSTRICO
Relaxamento
receptivo do
fundo gástrico
(nervos
parassimpáticos)
Armazenamento
do bolo alimentar
no fundo e no
corpo

MOTILIDADE GÁSTRICA
Fragmenta e mistura o bolo alimentar com as secreções
gástricas
Esvazia gradativamente o quimo (bolo alimentar) no
duodeno

ENCHIMENTO
GÁSTRICO
Relaxamento
receptivo do
fundo gástrico
(nervos
parassimpáticos)
Armazenamento
do bolo alimentar
no fundo e no
corpo

MISTURA DO
CONTEÚDO GÁSTRICO

Duodeno
ÁCIDO HIPERTONICIDADE GORDURAS AMINOÁCIDOS
MENOR ESVAZIAMENTO GÁSTRICO
CCK, GIP gastrinasecretina
CCK = colecistocinina
GIP = peptídeo inibidor gástrico
ESVAZIAMENTO GÁSTRICO

SECREÇÕES GÁSTRICAS
Células mucosas: muco
Células parietais ou
oxínticas: ácido clorídrico e
fator intrínseco
Células principais ou
pépticas: pepsinogênio
Células G: gastrina

SECREÇÃO DE ÁCIDO

SECREÇÃO DE ENZIMAS
HCl
pepsinogênio pepsina
pepsinogênio pepsina

DIGESTÃO GÁSTRICA
Polipeptídeos
Oligopeptídeos
PEPSINAS DO SUCO GÁSTRICO

SECREÇÃO DE MUCO

FASE GÁSTRICA FASE INTESTINAL
VisãoOlfato
Paladar
Distensão e aminoácidos no estômago
Acidez, gorduras, hipertonicidade e
irritação no duodeno
Nervos parassimpáticos
Gastrina
Histamina
Nervos
parassimpáticos
Gastrina
Distensão e aminoácidos no duodeno
Secretina
CCK
GIP
AUMENTO DA SECREÇÃO GÁSTRICAREDUÇÃO DA
SECREÇÃO GÁSTRICA
FASE CEFÁLICA
CONTROLE DAS SECREÇÕES GÁSTRICAS

Movimentos de Mistura
HAUSTRAÇÕES
Movimentos de Mistura
HAUSTRAÇÕES
Movimentos Propulsivos
DE MASSA
Movimentos Propulsivos
DE MASSA
***************PADRÕES DE MOTILIDADE NO TRATO****************
***************PADRÕES DE MOTILIDADE NO TRATO****************
MOTILIDADE INTESTINALMOTILIDADE INTESTINAL

CONTROLE DA MOTILIDADE DO INTESTINO GROSSO
DISTENSÃO DO ESTÔMAGO
DISTENSÃO DO DUODENO
Nervos Parassimpáticos
MOVIMENTOS DE MASSA

SECREÇÕES DO INTESTINO GROSSO
Secreções mucosas:
Adesão ao bolo fecal
Facilitação do deslizamento do bolo fecal
Proteção contra irritação mecânica e química do epitélio
PROCESSOS ABSORTIVOS DO INTESTINO GROSSO
Absorção de eletrólitos
Absorção de água

RETO E CANAL ANAL

DEFECAÇÃO
Movimento de massa no colo
sigmóide
Enchimento do Reto
Nervos parassimpátic
os sacrais
RELAXAMENTO DO ESFÍNCTER ANAL
INTERNO
Córtex cerebral
Nervos somáticos
RELAXAMENTO DO ESFÍNCTER ANAL
EXTERNO
INSPIRAÇÃO PROFUNDA E
CONTRAÇÃO DOS MÚSCULOS
TORÁCICOS E ABDOMINAIS