IV Guía CCNA SecurityV4
-
Upload
saulga-jardo -
Category
Documents
-
view
227 -
download
9
description
Transcript of IV Guía CCNA SecurityV4
CCNP 1 OSPF
Guia CCNA Security v2
CBAC2Zone Based Firewall I4Zone Based Firewall II9Zone Based Firewall III14
CBAC
CBAC inspecciona los flujos de trfico entre zonas de confianza y zonas inseguras, permite el trfico desde una zona insegura a una zona de confianza siempre que ese flujo se haya iniciado en la zona de confianza.
Setup: Configure direccionamiento mostradoConfigure RIPv2 para que exista NLRI extremo/extremo.
Configure R1 para que permita el trfico TCP, UDP, ICMP iniciado desde la red INSIDE a la red OUTSIDE. Desde la red OUTSIDE se permite trafico ICMP y Telnet siempre que el destino sea la IP 10.1.123.3/24 (R3). El resto del trfico desde la red OUTSIDE debe ser denegado.
Nota: Tenemos que definir dos polticas para este escenario: Inside OUTSIDE OUTSIDE INSIDE
R1Estos comandos le dicen al IOS que inspeccione el trfico TCP, UDP e ICMP. CBAC no monitorea lo que sucede en el instante sobre la conexin, si es requerido, una inspeccin especfica para una aplicacin dada puede ser configurada, una vez configurada toma prescedencia sobre la inspeccin genrica TCP o UDP.
ip inspect name OUT tcpip inspect name OUT udpip inspect name OUT icmp
Las ACLs permiten cualquier trfico desde la red 10.1.123.0/24 a cualquier red, tambin permite que RIPv2 opere.
access-list 100 permit ip 10.1.123.0 0.0.0.255 anyaccess-list 100 permit udp any any eq rip
interface FastEthernet0/0 description **INTERFACE INSIDE** ip inspect OUT in ip access-group 100 in
Puesto que solo se permite el trfico Telnet e ICMP desde la red insegura debemos identificarlo con otra ACL.
R1access-list 101 permit icmp any host 10.1.123.3access-list 101 permit tcp any host 10.1.123.3 eq telnetaccess-list 101 permit udp any any eq 520
interface FastEthernet0/1 description **INTERFACE OUTSIDE**ip access-group 101 in
Configure telnet en R3. Cree usuario admin password class. El usuario necesite acceder a R3 a travs de telnet debe loguearse utilizando la base de datos local. Use password cisco para acceder a modo privilegiado.
R3username admin password class
enable secret cisco
aaa new-modelaaa authentication login TELNET local
line vty 0 4 login authentication TELNET
Pruebas CBAC. Desde R2 a R4 acceder por telnet. Comprobar que existe inspeccin utilizando el comando sh ip inspect con argumento necesario. R4 debe poder acceder remotamente a R3 usando telnet y comprobar conectividad utilizando ping.
Zone Based Firewall I
Setup: Configure direccionamiento mostrado Configure RIPv2 para que exista NLRI extremo/extremo. Verificar utilizando la tabla de enrutamiento y comprobar cada red creada.
Configure R1 con las siguientes polticas: Permitir todo el trfico TCP, UDP e ICMP siempre que sea iniciado desde la red INSIDE a la DMZ y la red OUTSIDE. El trfico que no sea iniciado desde la red INSIDE debe ser denegado. Permitir solo el trfico ICMP y HTTP iniciado desde la red OUTSIDEa la DMZ.
R1router rip version 2 network 10.0.0.0 network 200.1.1.0 no au
R2router rip version 2 network 10.0.0.0 no au
R3router rip version 2 network 200.1.1.0 no au
R4router rip version 2 network 10.0.0.0 no au
R3#sh ip route rip 10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 4 subnetsR 10.1.14.0 [120/1] via 200.1.1.1, 00:00:07, Serial1/0R 10.1.12.0 [120/1] via 200.1.1.1, 00:00:07, Serial1/0R 10.4.4.0 [120/2] via 200.1.1.1, 00:00:07, Serial1/0R 10.2.2.0 [120/2] via 200.1.1.1, 00:00:07, Serial1/0
1. En R1 definimos elo trfico interesante utilizando el class-map desde la INSIDE a la OUTSIDE.
R1class-map type inspect match-any CM-INSIDE match protocol tcp match protocol udp match protocol icmp
class-map type inspect match-any CM-OUTSIDE match protocol http match protocol icmp
2. Este segundo paso nos permite determinar que hacer con el trfico interesante que definimos con el class-map (permitirlo, inspeccionarlo, descartarlo, entre otras opciones). En R1 aplicamos las polticas respetando la direccin de cada una de ellas. INSIDEoutside, INSIDEdmz, OUTSIDEDMZ.
R1policy-map type inspect PM-INSIDE-TO-OUTSIDE class type inspect CM-INSIDE inspect
policy-map type inspect PM-INSIDE-TO-DMZ class type inspect CM-INSIDE inspect
policy-map type inspect PM-OUTSIDE-TO-DMZ class type inspect CM-OUTSIDE inspect
3. Definimos las zonas de seguridad INSIDE, OUTSIDE y DMZ. En este caso se han asignado los nombres de las zonas en minsculas salvo la DMZ.
R1zone security insidezone security outsidezone security DMZ
4. En este paso asignamos las zonas a las interfaces apropiadas. Recordar que los nombres fueron asignados con minsculas.
R1interface FastEthernet0/0 zone-member security inside
interface Serial1/0 zone-member security outside
interface FastEthernet0/1 zone-member security DMZ
5. El ltimo paso consiste en asociar polticas entre zonas (zone-pair). Que en pocas palabras define direccionalidad del trfico.
R1zone-pair security Z-IO source inside destination outside service-policy type inspect PM-INSIDE-TO-OUTSIDE
zone-pair security Z-ID source inside destination DMZ service-policy type inspect PM-INSIDE-TO-DMZ
zone-pair security Z-OD source outside destination DMZ service-policy type inspect PM-OUTSIDE-TO-DMZ
Pruebas ICMP Ping desde R2 (INSIDE) a R4 (DMZ)OK Ping desde R2 (INSIDE) a R3 (OUTSIDE)OK Ping desde R3 (OUTSIDE) a R2 (INSIDE)FAIL Ping desde R3 (OUTSIDE) a R4 (DMZ)OK
R2#ping 10.1.14.4Type escape sequence to abort.Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.14.4, timeout is 2 seconds:!!!!!Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 52/68/84 ms
R2#ping 200.1.1.3Type escape sequence to abort.Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 200.1.1.3, timeout is 2 seconds:!!!!!Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 56/67/92 msR3#ping 10.1.12.2Type escape sequence to abort.Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.12.2, timeout is 2 seconds:.....Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)
R3#ping 10.1.14.4Type escape sequence to abort.Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.14.4, timeout is 2 seconds:!!!!!Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 52/66/92 ms
R1#show policy-map type inspect zone-pair Z-ID Zone-pair: Z-ID
Service-policy inspect : PM-INSIDE-TO-DMZ
Class-map: CM-INSIDE (match-any) Match: protocol tcp 0 packets, 0 bytes 30 second rate 0 bps Match: protocol udp 0 packets, 0 bytes 30 second rate 0 bps Match: protocol icmp1 packets, 80 bytes30 second rate 0 bps Inspect Packet inspection statistics [process switch:fast switch] icmp packets: [0:10]
Session creations since subsystem startup or last reset 1 Current session counts (estab/half-open/terminating) [0:0:0] Maxever session counts (estab/half-open/terminating) [1:1:0] Last session created 00:06:44 Last statistic reset never Last session creation rate 0 Maxever session creation rate 1 Last half-open session total 0
Class-map: class-default (match-any) Match: any Drop (default action)0 packets, 0 bytes
Pruebas TCP utilizando Telnet (habilitar telnet en todos los routers de la topologa). Telnet desde R2 (INSIDE) a R4 (DMZ)OK Telnet desde R2 (INSIDE) a R3 (OUTSIDE)OK Telnet desde R3 (OUTSIDE) a R2 (INSIDE)FAIL HTTP desde R3 (OUTSIDE) a R4 (DMZ)OK
R1#telnet 10.1.14.4Trying 10.1.14.4 ... OpenR4>
R1#telnet 200.1.1.3Trying 200.1.1.3 ... OpenR3>
R3#telnet 10.1.12.2Trying 10.1.12.2 ...% Connection timed out; remote host not responding
Para poder testear la coneccin HTTP debe habilitar a R4 como server para HTTP. A pesar de que NO obtendremos acceso a travs de telnet, si existe un servicio abierto (Open) que corresponde a HTTP. La salida que nos entrega el comando show policy-map type inspect zone-pair Z-OD nos muestra este comportamiento. R4ip http server
R3#telnet 10.1.14.4 80Trying 10.1.14.4, 80 ... Open
R1#show policy-map type inspect zone-pair Z-OD Zone-pair: Z-OD
Service-policy inspect : PM-OUTSIDE-TO-DMZ
Class-map: CM-OUTSIDE (match-any) Match: protocol http1 packets, 24 bytes 30 second rate 0 bps Match: protocol icmp1 packets, 80 bytes 30 second rate 0 bps Inspect Packet inspection statistics [process switch:fast switch] tcp packets: [0:11] icmp packets: [0:10]
Session creations since subsystem startup or last reset 2 Current session counts (estab/half-open/terminating) [1:0:0] Maxever session counts (estab/half-open/terminating) [1:1:0] Last session created 00:04:36 Last statistic reset never Last session creation rate 0 Maxever session creation rate 1 Last half-open session total 0
Class-map: class-default (match-any) Match: any Drop (default action)4 packets, 96 bytes
Zone Based Firewall II
Nota: Utilizar Plataforma 3725Setup: Cree el direccionamiento mostrado. Configure EIGRP 1 para lograr conectividad extremo a extremo. Desactive sumarizacin automtica. Habilite telnet en R4 y R3. Habilite SSH v1.9 en R2 y R5 (genere valores y usuarios arbitrariamente).
Configure R1 con ZPF utilizando las siguientes polticas: Permitir todo el trfico TCP, UDP e ICMP siempre que sea iniciado desde la red INSIDE a la DMZ y desde la INSIDE a la red OUTSIDE. El trfico que no sea iniciado desde la red INSIDE debe ser denegado. Habilite a R1 para que enve mensajes de log INSPECT a la consola y al servidor syslog (ip inspect log drop-pkt). R3 debe acceder a la zona INSIDE utilizando SSH.
SETUP: EIGRP 1, SSHv2
R1router eigrp 1 network 10.0.0.0 network 200.1.1.0 no auto-summary
R2router eigrp 1 network 10.0.0.0 no auto-summary
R3router eigrp 1 network 200.1.1.0 no auto-summary
R4router eigrp 1 network 10.0.0.0 no auto-summary
R5router eigrp 1 network 10.0.0.0 no auto-summary
R1#show ip eigrp neighborsIP-EIGRP neighbors for process 1H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq (sec) (ms) Cnt Num3 10.1.15.5 Fa2/0 12 00:00:44 112 672 0 42 10.1.14.4 Fa0/1 14 00:00:51 113 678 0 31 200.1.1.3 Se1/0 11 00:00:59 77 462 0 30 10.1.12.2 Fa0/0 12 00:01:04 108 648 0 3
R2enable secret ciscousername admin password ciscoip domain-name duoc.clcrypto key generate rsa usage-keys
aaa new-modelaaa authentication login VTY-LOCAL local
line vty 0 4 login authentication VTY-LOCAL transport output sshR2enable secret ciscousername admin password ciscoip domain-name duoc.clcrypto key generate rsa usage-keys
aaa new-modelaaa authentication login VTY-LOCAL local
line vty 0 4 login authentication VTY-LOCALtransport output ssh
1. En R1 definimos elo trfico interesante utilizando el class-map desde la INSIDE a la OUTSIDE.
R1class-map type inspect match-any CM-INSIDE match protocol tcp match protocol udp match protocol icmp
class-map type inspect match-any CM-OUTSIDEmatch protocol ssh
2. Este segundo paso nos permite determinar que hacer con el trfico interesante que definimos con el class-map (permitirlo, inspeccionarlo, descartarlo, entre otras opciones). En R1 aplicamos las polticas respetando la direccin de cada una de ellas. INSIDEoutside, INSIDEdmz, OUTSIDEDMZ.
R1policy-map type inspect PM-INSIDE-TO-OUTSIDE class type inspect CM-INSIDE inspect
policy-map type inspect PM-INSIDE-TO-DMZ class type inspect CM-INSIDE inspect
policy-map type inspect PM-OUTSIDE-TO-INSIDE class type inspect CM-OUTSIDE inspect
3. Definimos las zonas de seguridad INSIDE, OUTSIDE y DMZ. En este caso se han asignado los nombres de las zonas en minsculas salvo la DMZ.
R1zone security insidezone security outsidezone security DMZ
4. En este paso asignamos las zonas a las interfaces apropiadas. Recordar que los nombres fueron asignados con minsculas.
R1interface FastEthernet0/0 zone-member security inside
interface FastEthernet2/0zone-member security inside
interface Serial1/0 zone-member security outside
interface FastEthernet0/1 zone-member security DMZ
5. El ltimo paso consiste en asociar polticas entre zonas (zone-pair). Que en pocas palabras define direccionamiento del trfico.
R1zone-pair security Z-IO source inside destination outside service-policy type inspect PM-INSIDE-TO-OUTSIDE
zone-pair security Z-ID source inside destination DMZ service-policy type inspect PM-INSIDE-TO-DMZ
zone-pair security Z-OD source outside destination inside service-policy type inspect PM-OUTSIDE-TO-INSIDE
ip inspect log drop-pkt
Pruebas ICMP Ping desde R2 (INSIDE) a R4 (DMZ)OK Ping desde R5 (INSIDE) a R4 (DMZ)OK Ping desde R2 (INSIDE) a R3 (OUTSIDE)OK Ping desde R3 (OUTSIDE) a R2 (INSIDE)FAIL Ping desde R3 (OUTSIDE) a R5 (INSIDE)FAIL
R2#ping 10.1.14.4Type escape sequence to abort.Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.14.4, timeout is 2 seconds:!!!!!Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 60/68/92 ms
R5#ping 10.1.14.4Type escape sequence to abort.Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.14.4, timeout is 2 seconds:!!!!!Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 36/68/92 ms
R2#ping 200.1.1.3Type escape sequence to abort.Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 200.1.1.3, timeout is 2 seconds:!!!!!Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 56/65/84 ms
R3#ping 10.1.12.2Type escape sequence to abort.Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.12.2, timeout is 2 seconds:.....Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)
R3#ping 10.1.15.5Type escape sequence to abort.Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.15.5, timeout is 2 seconds:.....Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)
R1#%FW-6-DROP_PKT: Dropping icmp session 200.1.1.3:0 10.1.15.5:0 on zone-pair Z-OD class class-default due to policy match failure with ip ident 30
Prueba SSH OUTSIDEINSIDE
R3#ssh -l admin -c 3des 10.2.2.2Password:cisco
R2>enablePassword:ciscoR2#exit
R1#%FW-6-DROP_PKT: Dropping Other session 200.1.1.3:50226 10.2.2.2:22 due to Stray Segment with ip ident 37207 tcpflags 0x5004 seq.no 3158919498 ack 0
Zone Based Firewall III
Nota: Utilizar Plataforma 3725Setup: Cree el direccionamiento mostrado. Configure EIGRP 1 para lograr conectividad extremo a extremo. Desactive sumarizacin automtica. En todos los routers debemos acceder via telnet usando la pasword cisco del modo privilegiado.
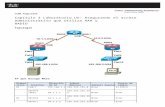
Configure R1 con ZPF utilizando las siguientes polticas: Los routers de la zona INSIDE deben acceder a R3 (OUTSIDE) va telnet utilizando sus loopback0 como origen.(R210.2.2.2/32 y R5 10.5.5.5). No configurar R3 para esta regla. Se permite solo el trfico TFTP desde la zona OUTSIDE a la INSIDE. Enviar la configuracin completa al servidor TFTP que muestra la figura. Habilite NMAP para R1 y verifique puertos habilitados/deshabilitados.
R1router eigrp 1 network 10.0.0.0 network 200.1.1.0 no auto-summary
R2router eigrp 1 network 10.0.0.0 no auto-summaryR3router eigrp 1 network 10.0.0.0 network 200.1.1.0 no auto-summary
R4router eigrp 1 network 10.0.0.0 no auto-summary
R5router eigrp 1 network 10.0.0.0 network 100.0.0.0 no auto-summary
R1#show ip eigrp neighborsIP-EIGRP neighbors for process 1H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq (sec) (ms) Cnt Num3 10.1.15.5 Fa2/0 14 00:18:00 92 552 0 72 10.1.14.4 Fa0/1 14 00:18:14 135 810 0 61 200.1.1.3 Se1/0 11 00:18:18 113 678 0 70 10.1.12.2 Fa0/0 14 00:18:26 94 564 0 7
R1#sh ip route eigrp 100.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnetsD 100.1.1.0 [90/284160] via 10.1.15.5, 00:19:07, FastEthernet2/0 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 7 subnets, 2 masksD 10.4.4.0/24 [90/409600] via 10.1.14.4, 00:19:20, FastEthernet0/1D 10.2.2.0/24 [90/409600] via 10.1.12.2, 00:19:32, FastEthernet0/0D 10.5.5.5/32 [90/156160] via 10.1.15.5, 00:00:28, FastEthernet2/0
R1aaa new-modelaaa authentication login TELNET enableenable secret cisco
line vty 0 4 login authentication TELNET
R2aaa new-modelaaa authentication login TELNET enableenable secret cisco
line vty 0 4 login authentication TELNET
R3aaa new-modelaaa authentication login TELNET enableenable secret cisco
line vty 0 4 login authentication TELNET
R4aaa new-modelaaa authentication login TELNET enableenable secret cisco
line vty 0 4 login authentication TELNET
R5aaa new-modelaaa authentication login TELNET enableenable secret cisco
line vty 0 4 login authentication TELNET
R5#telnet 10.1.1.1Trying 10.1.1.1 ... OpenUser Access VerificationPassword:cisco
R1>enablePassword:cisco
Los routers de la zona INSIDE deben acceder a R3 (OUTSIDE) va telnet. Ut
R1access-list 100 permit ip host 10.2.2.2 anyaccess-list 100 permit ip host 10.5.5.5 any
class-map type inspect match-allCM-INSIDEmatch protocol telnet match access-group 100
class-map type inspect match-any CM-DMZmatch protocol tftp
1. Este segundo paso nos permite determinar que hacer con el trfico interesante que definimos con el class-map (permitirlo, inspeccionarlo, descartarlo, entre otras opciones). En R1 aplicamos 2 polticas: INSIDEoutside, DMZINSIDE.
R1policy-map type inspect PM-INSIDE-TO-OUTSIDE class type inspect CM-INSIDE inspect
policy-map type inspect PM-DMZ-TO-INSIDE class type inspect CM-DMZ inspect
2. Definimos las zonas de seguridad INSIDE, OUTSIDE y DMZ. En este caso se han asignado los nombres de las zonas en minsculas salvo la DMZ.
R1zone security insidezone security outsidezone security DMZ
3. En este paso asignamos las zonas a las interfaces apropiadas. Recordar que los nombres fueron asignados con minsculas.
R1interface FastEthernet0/0 zone-member security inside
interface FastEthernet2/0 zone-member security inside
interface Serial1/0 zone-member security outside
interface FastEthernet0/1 zone-member security DMZ
4. El ltimo paso consiste en asociar polticas entre zonas (zone-pair). Que en pocas palabras define direccionalidad del trfico.
R1zone-pair security Z-IO source inside destination outside service-policy type inspect PM-INSIDE-TO-OUTSIDE
zone-pair security Z-DI source DMZ destination inside service-policy type inspect PM-DMZ-TO-INSIDE
ip inspect log drop-pktip inspect audit-trail
Pruebas Syslog
R1logging onlogging origin-id hostnamelogging source-interface loopback0logging 100.1.1.11logging trap debugging
18
@ NMT 2013